Alpaca Origins
Alpacas originated from South America and are a member of the camelid family, the largest percentage coming from Peru and Chile. They are related to camels, Llamas, vicunas and guanacos. Alpacas have been valued for their soft luxurious fleeces for generations, indeed their fleece has been called ‘the fibre of the gods’.
Alpaca fibre was so valued by early South American civilisations that it was used as a form of currency.
Alpaca Terms
- Male – Machos
- Female – Hembra
- Baby Alpaca – Cria
- Birthing – Unpacking
Farming Alpacas
Alpacas are herd animals, therefore you require at least two. Stocking Rate is normally quoted as being similar to sheep (around 4-5 per acre) Alpacas are very efficient food converters
Alpacas eat pasture grass and hay. They are easy care, compared to other stock species and are very low maintenance, ideal for people with limited farming experience, yet add diversity to larger farming operations.
Shearing is once a year, at Nevalea Alpacas, Neville shears our alpacas on a table.


Animal Health – remarkably disease free, require annual inoculations, toenail trimming as required, worming once or twice a year, and vitamin A, D&E injection
Alpacas do not get bloat, flystrike or footrot. Fencing, normal farm fences are adequate. Shelter, trees to protect from wind and sun in New Zealand’s moderate climatic.
Alpacas are induced ovulators. This means that they do not have a cycle, and can be mated at any time they are not pregnant, as a female is receptive to the male then. The female is induced to ovulate by the actions of the male.
Alpacas can start breeding – females at 12 months old, if they weigh over 40kg and are ready for mating.
– Males generally do not start breeding until 2-3 years old.
Physical Characteristics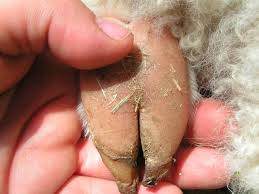
- Alpacas have soft padded feet, making them gentle on the land
- They have two toenails on each foot
- They have a split upper lip (like a rabbit) which enables them to cleverly nibble around long and sharp thorns
- The chew their cud like a cow, they are a ruminant
- Alpacas are very gentle animals
Alpaca Types – There are Two
- Suri – has a distinctive fleece that grows parallel to the body in long, silky ringlet-like locks.
- Huacaya – has thick dense fleece, growing vertically from the body, giving it a very soft woolly appearance. The fleece can be manufactured into either textiles or yarn
Life Span
Alpacas have a life span in New Zealand of between 12 & 20 years depending on environment
Gestation
An alpaca’s gestation period is 11 to 12 months, about 335 days
They have single births (twins are rare)
Cria are normally born without assistance between 10am and 3pm on warm, fine days
A Cria, usually weights between 5-8kg at birth
Fleece
Alpaca fibre comes in 22 shades of colour, recognised by the textile industry
Has low scratch factor, is more thermal and has higher tensile strength than sheep’s wool
An Alpaca can produce 2kg – 5kg of soft warm fibre every year
Clean fleece retails for premium prices
High quality fibre is high demand in the fashion industry worldwide




